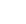Access to Collaboration Site and Physics Results
ATLAS Briefings
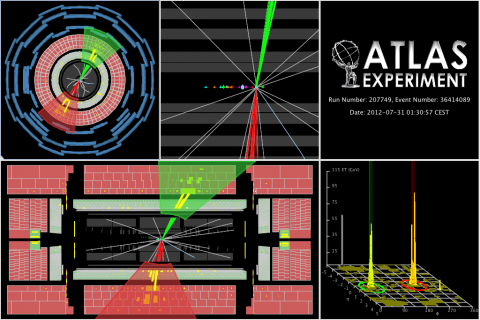
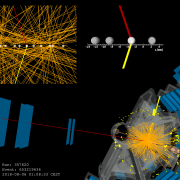
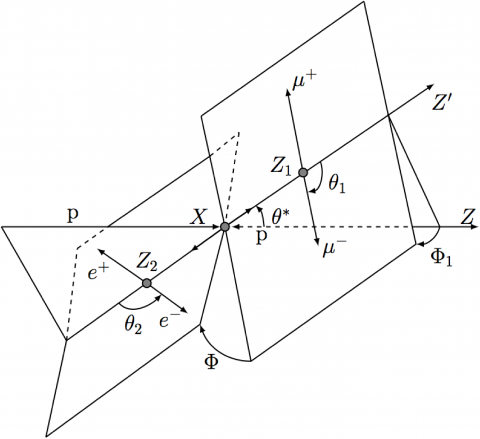
Run 1 search for new massive bosons builds excitement for Run 2
– The ATLAS experiment is now taking data from 13 TeV proton-proton collisions. The increased collision energy and rate in these Run 2 collisions will allow physicists to carry out stronger tests of many theoretical conjectures, including several theories that predict more massive versions of force-carrying particles like the W and Z bosons.Read more →
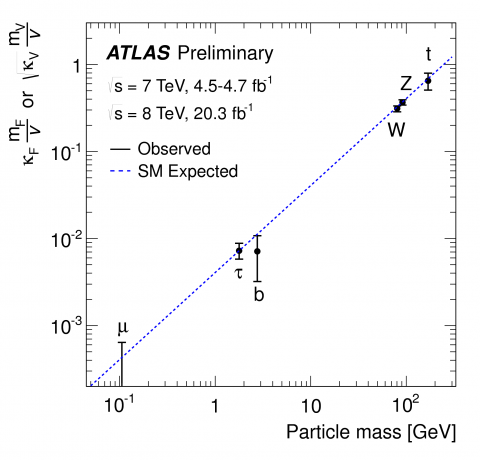
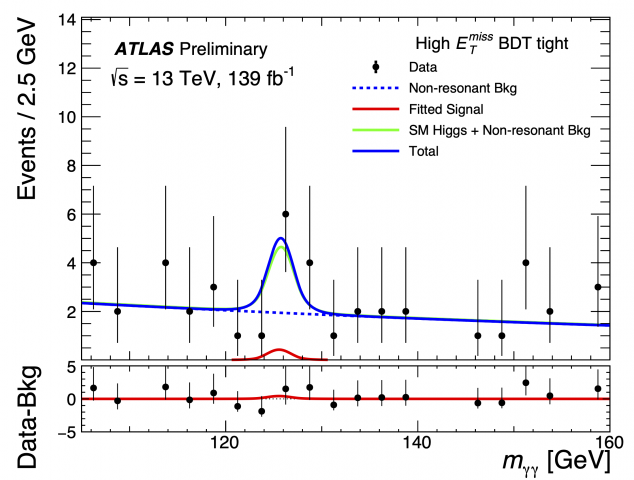
ATLAS further verifies Standard Model coupling/mass relationship of Higgs boson
– The discovery of a Higgs Boson in 2012 by the ATLAS and CMS experiments marked a key milestone in the history of particle physics. It confirmed a long-standing prediction of the Standard Model, the theory that underlines our present understanding of elementary particles and their interactions.Read more →
The scalar boson
– The ATLAS experiment has released results confirming that the Higgs boson has spin 0 (it is a so-called “scalar”) and positive parity as predicted by the Standard Model, making it the only elementary scalar particle to be observed in nature.Read more →
In search of rare Higgs boson production with top quarks
– In proton-proton collisions, several processes can lead to the production of a Higgs boson. The most “frequent” process (which is about one collision in four billion!) is the fusion of two gluons, contained in the initial protons, into a Higgs boson through a “top-quark loop”. Least frequent is a mode where the Higgs boson is produced in association with a pair of top-quarks.Read more →
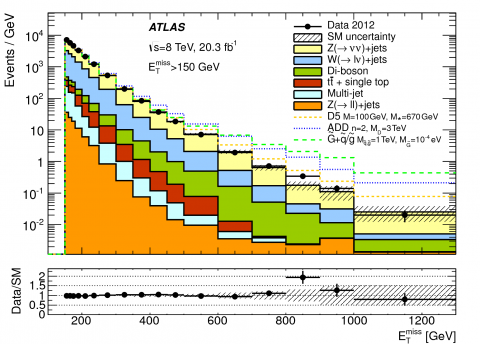
Looking at the Dark side of Matter
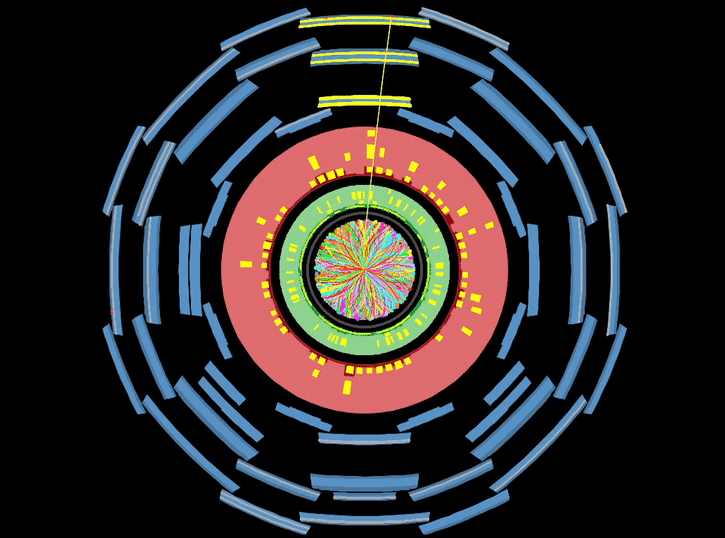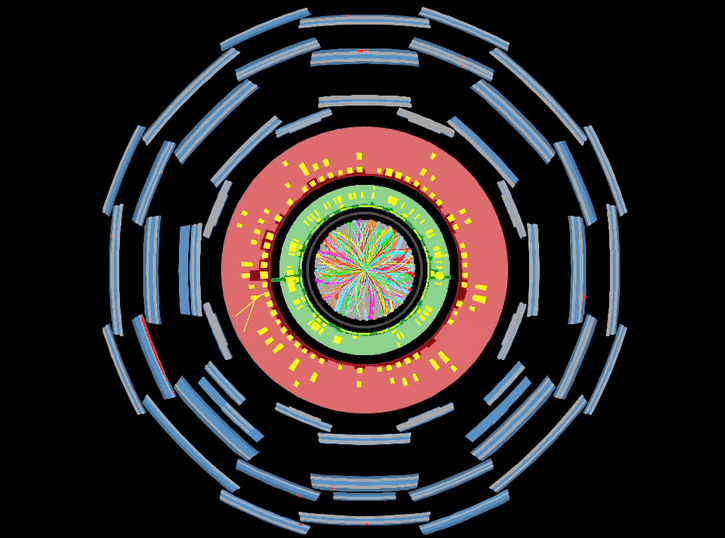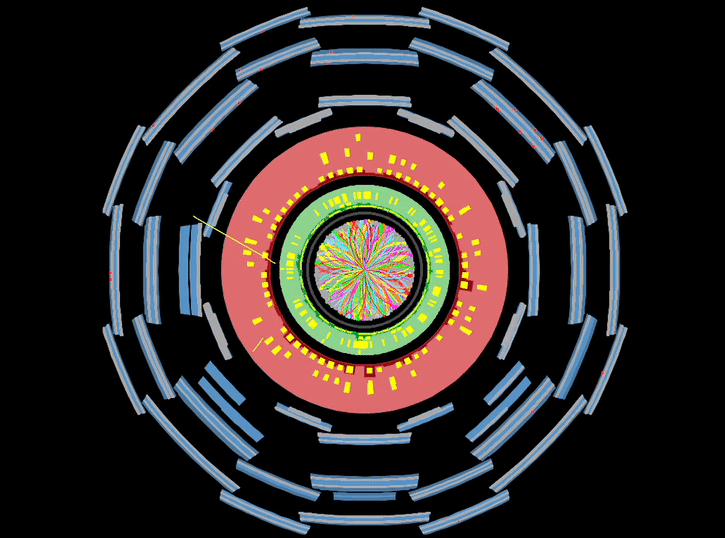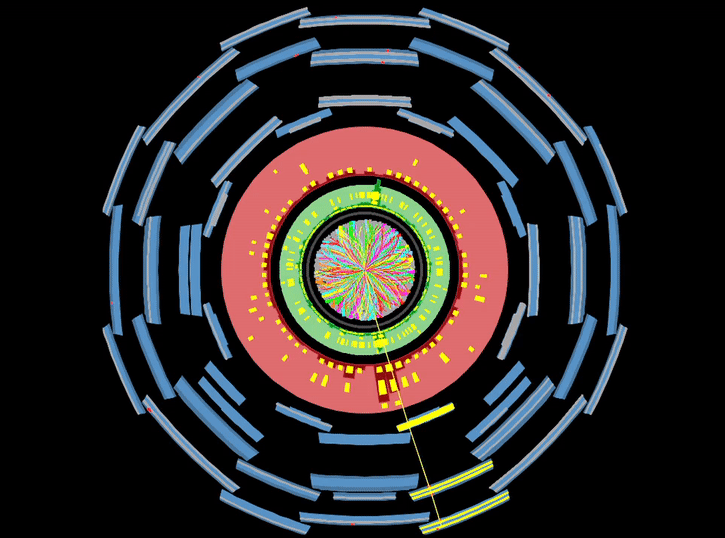
– The search continues for dark matter, a new kind of matter that doesn’t emit or absorb light. It is assumed to account for the missing amount of mass in our Universe. The total mass in our Universe can be inferred from the observation of gravitational effects of stars in galaxies, and galaxies in clusters of galaxies. However the amount of mass calculated from the observed distribution of light is much less. It is proposed that dark matter makes up the discrepancy as it does not emit light.Read more →
In search of super charm
– If all the experimental evidence supports a theory, why should anyone want to dream up additional particles? Yet exactly this situation arose in the late 1960s. At that time, when the complete table of the known hadrons could be explained with just three quarks, theorists were already proposing a fourth, which they whimsically called “charm”.Read more →
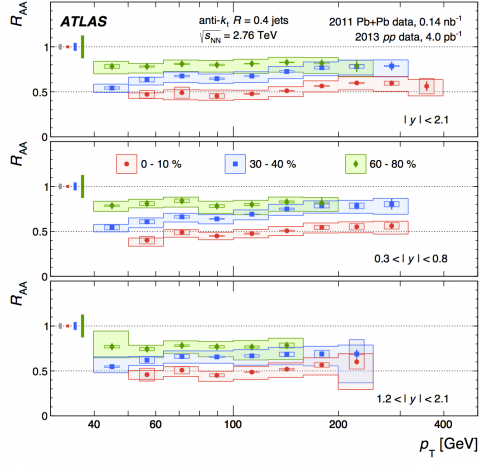
Quenching jets in the hot dense matter produced by colliding lead ions
– The Large Hadron Collider is known to collide protons, but for one month a year, beams of lead ions are circulated in the 27-km tunnel and made to collide in the centre of the experiments. The ATLAS experiment has made new precise measurements of the suppression of jets as they blast through the dense matter created by the lead ion collisions.Read more →
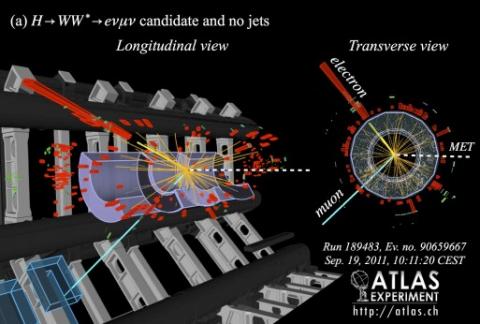
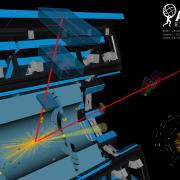
New ATLAS precision measurements of the Higgs boson: Observation of WW decay
– The Standard Model makes many different predictions regarding the production and decay properties of the Higgs boson, most of which can be tested at the Large Hadron Collider (LHC). Since the discovery, experimentalists from the ATLAS collaboration have analysed the complete dataset recorded in 2011 and 2012, have improved the calibration of the detector, and have increased substantially the sensitivity of their analyses.Read more →
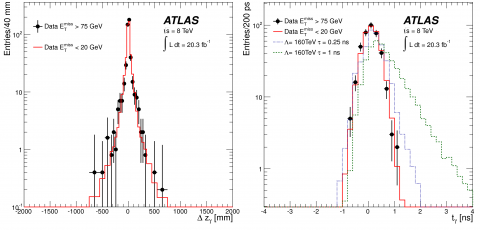
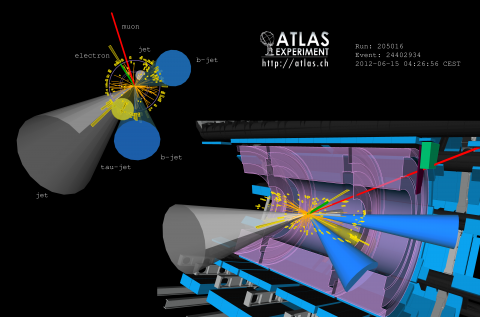
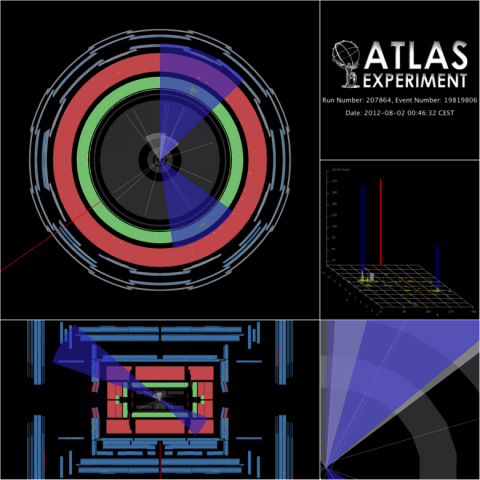
Searches for new physics with photons produced at vertices displaced from the collision point
– Theories, such as supersymmetry, propose the existence of new types of particles to explain important questions about the universe, such as the nature of dark matter. ATLAS has performed a search for one such type – exotic heavy particles that have lifetimes long enough that they travel partway through the detector before decaying, at what is called a displaced vertex.Read more →

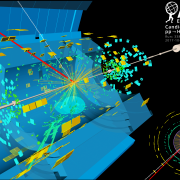
Higgs boson production measurements from the channels of discovery
– The discovery of the Higgs boson by the ATLAS and CMS collaborations in 2012 marked a new era in particle physics because it completed the Standard Model and gave us another tool to explore territories beyond. The Standard Model predicts precisely the interactions of the Higgs boson to all other elementary particles once its mass is measured.Read more →