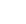Access to Collaboration Site and Physics Results
ATLAS Briefings
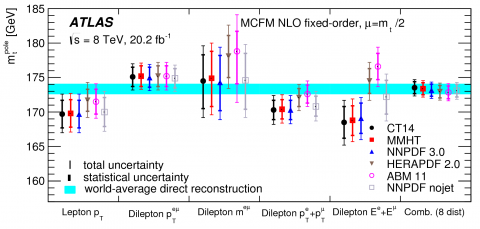
Studying fragments of the top quark
– Using Run 1 data, ATLAS reports a new differential production rate measurement of top quark pairs and a precise new determination of the top quark mass.Read more →
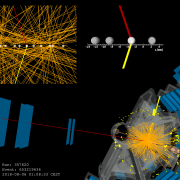
Hunting down forbidden decays of the top quark
– Ordinary matter is made of just three kinds of elementary particles: up and down quarks, which form the atomic nucleus, and electrons, which surround the nucleus. But the rest of nature is not so straightforward: heavier forms of quarks and leptons are produced regularly at particle accelerators.Read more →

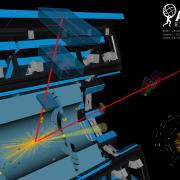
ATLAS and CMS look forward with the top quark
– The top quark, the heaviest known elementary particle, has a unique place in the Standard Model. By precisely measuring its properties, ATLAS physicists can probe physics beyond our current understanding.Read more →
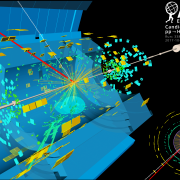
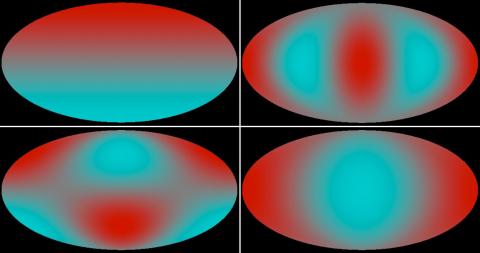
Finding a haystack in a field of haystacks
– In order to produce rare physics phenomena, such as the Higgs boson or possible signs of new physics, the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) collides tens of millions of protons per second. Under such conditions, around 20 simultaneous proton-proton interactions occur in each beam crossing. Thus, additional collisions called “pile-up” are recorded along with the collision of interest. Together, they form a single event for analysis.Read more →
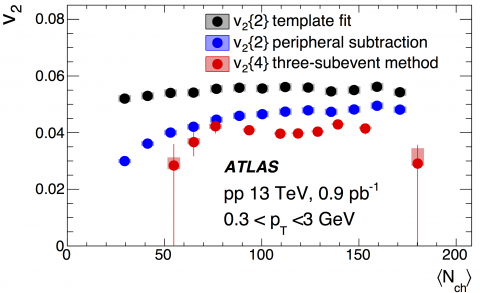
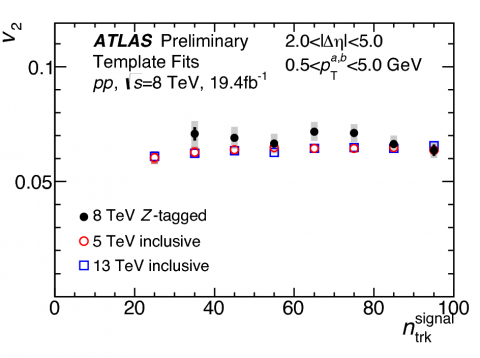
Exploring the nature of the “ridge” in small systems
– When ultra-relativistic heavy ions collide, a new state of hot and dense matter – the quark–gluon plasma (QGP) – is created. One of the key features for this state is the observation of long-range azimuthal angle correlations between particles emitted over a wide range of pseudorapidity. This phenomenon is often referred to as the “ridge”.Read more →
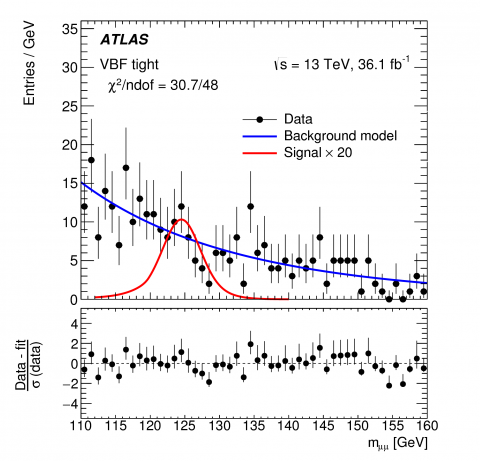
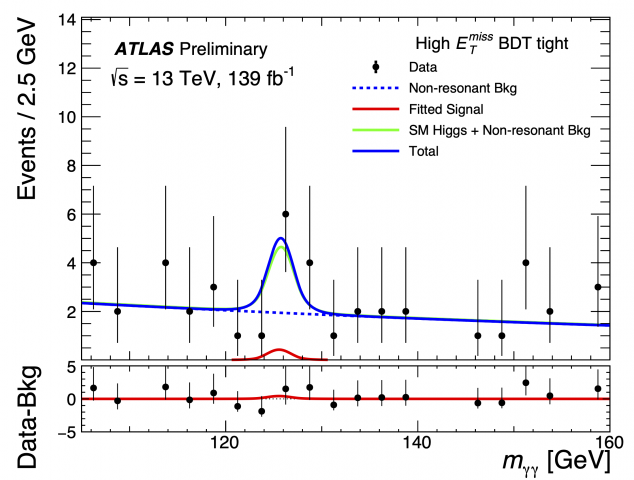
Exploring rare decays of the Higgs boson
– Since discovering a Higgs boson in 2012, the ATLAS and CMS collaborations have been trying to understand whether this new particle is the Higgs boson as predicted by the Standard Model, or a Higgs boson from a more exotic model containing new, as yet undiscovered, particles. The answer lies in the properties of the Higgs boson.Read more →
5 fundamental parameters from top quark decay
– For many physicists, discovering “new physics” means bringing to light a new particle. Another path to discovery lies in carefully measuring the properties of known particles and the interactions between them. The ATLAS experiment has now released new results on the top quark's interaction with the charged intermediate vector boson.Read more →
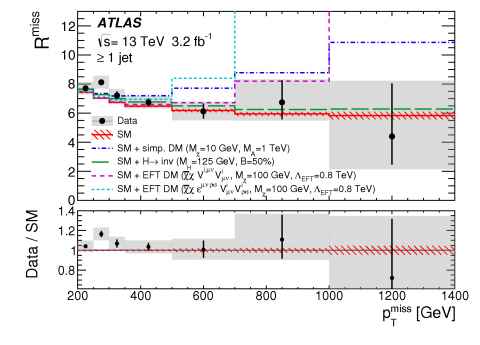
The invisible plan
– As the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) smashes together protons at a centre-of-mass energy of 13 TeV, it creates a rich assortment of particles that are identified through the signature of their interactions with the ATLAS detector. But what if there are particles being produced that travel through ATLAS without interacting? These “invisible particles” may provide the answers to some of the greatest mysteries in physics.Read more →

Probing physics beyond the Standard Model with heavy vector bosons
– Although the discovery of the Higgs boson by the ATLAS and CMS Collaborations in 2012 completed the Standard Model, many mysteries remain unexplained. For instance, why is the mass of the Higgs boson so much lighter than one would expect and why is gravity so weak?Read more →
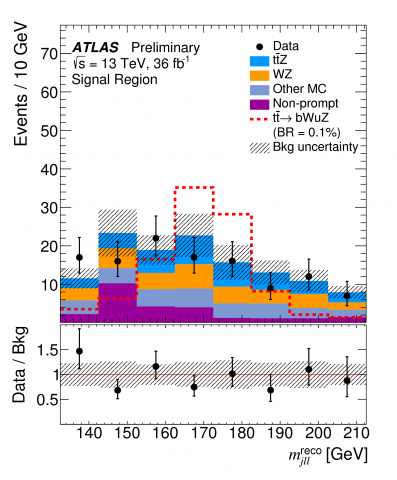
New rare pairs of heavy friends in ATLAS
– Observing rare productions of heavy elementary particles can provide fresh insight into the Standard Model of particle physics. In a new result, the ATLAS Experiment presents strong evidence for the production of a single top-quark in association with a Z boson.Read more →