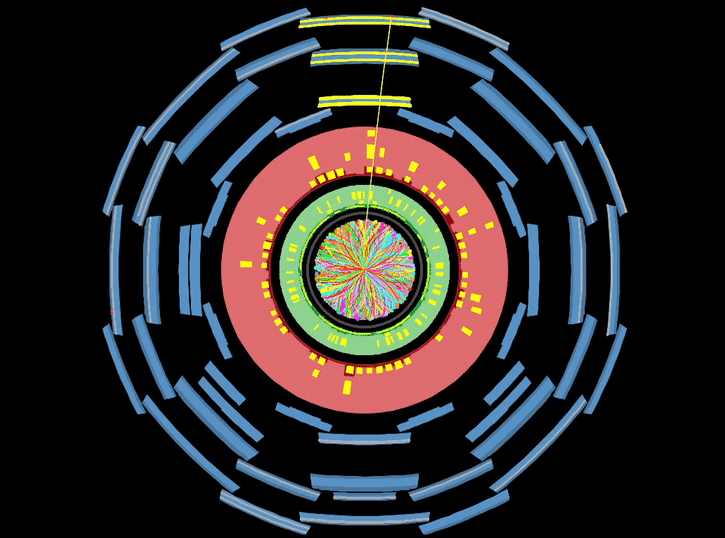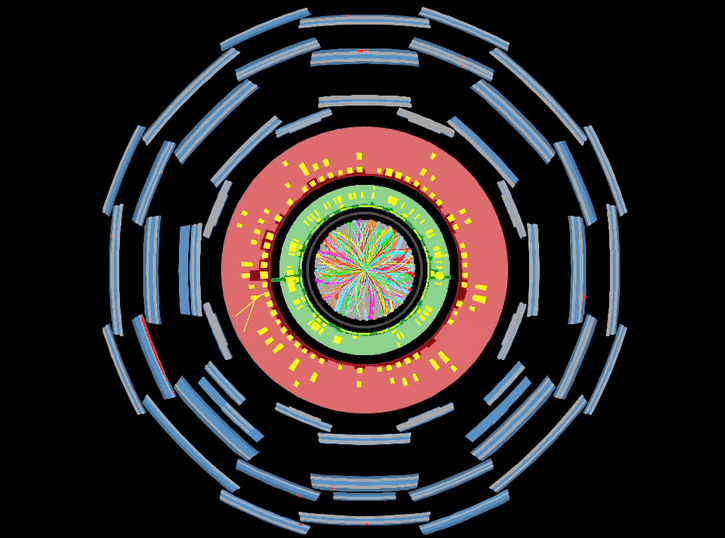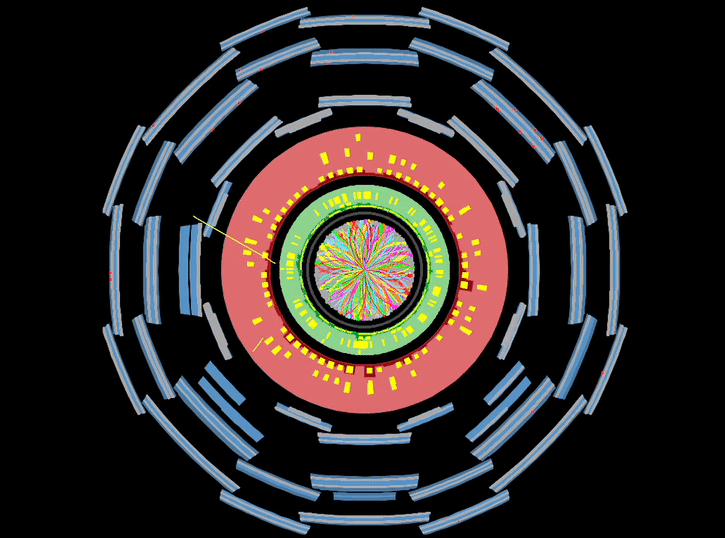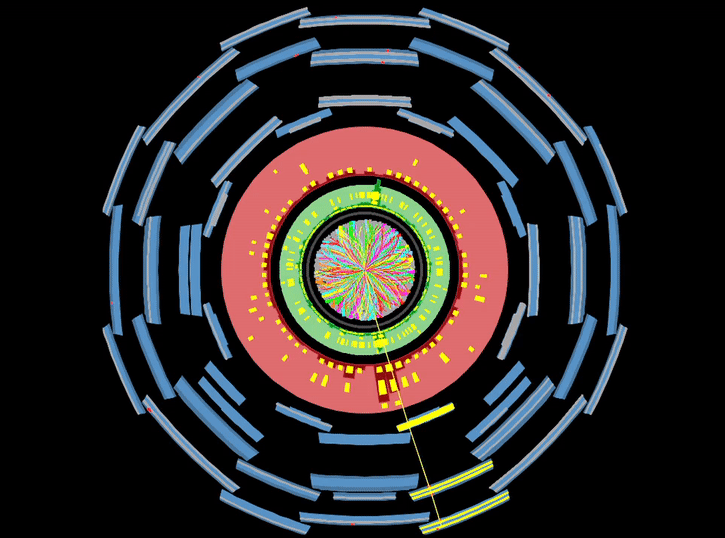
Access to Collaboration Site and Physics Results
Muon Spectrometer

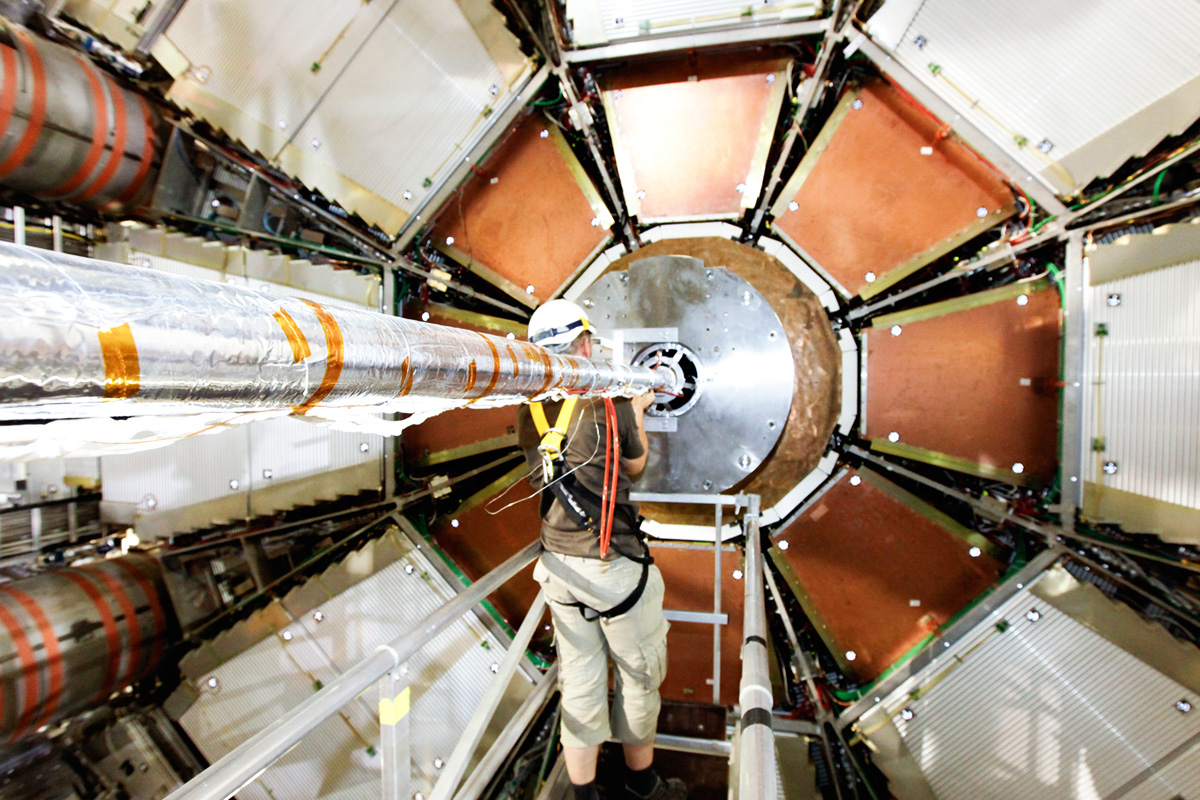
Muons are particles that usually pass through the Inner Detector and Calorimeter undetected. The muon spectrometer, made up of 4,000 individual muon chambers using four different technologies by 48 institutions in 23 production sites around the world, identifies and measures the momenta of muons.
Subsections of the Muon System: Thin Gap Chambers, Resistive Plate Chambers, Monitored Drift Tubes, and Cathode Strip Chambers.
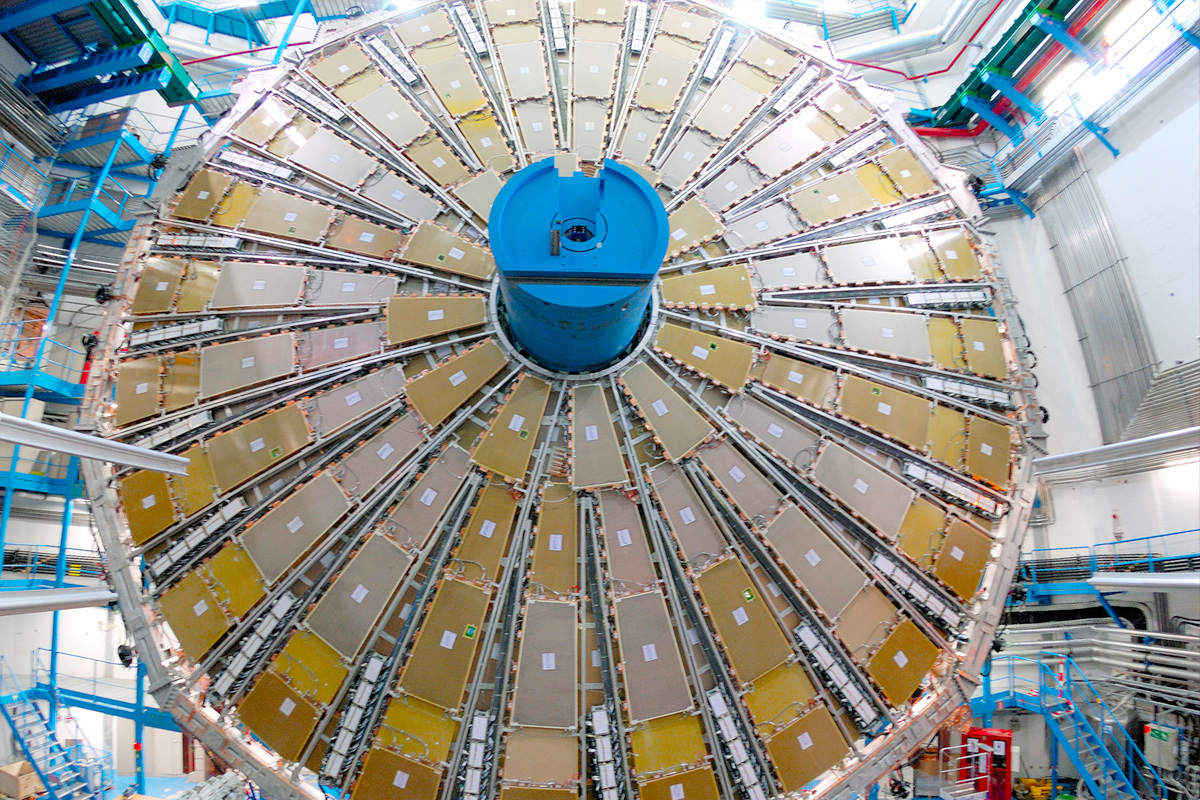
Thin Gap Chambers
- For triggering and 2nd coordinate measurement (non-bending direction) at ends of detector.
- 440,000 channels
Resistive Plate Chambers
- For triggering and 2nd coordinate measurement in central region.
- 380,000 channels
- Electric Field 5,000 V/mm
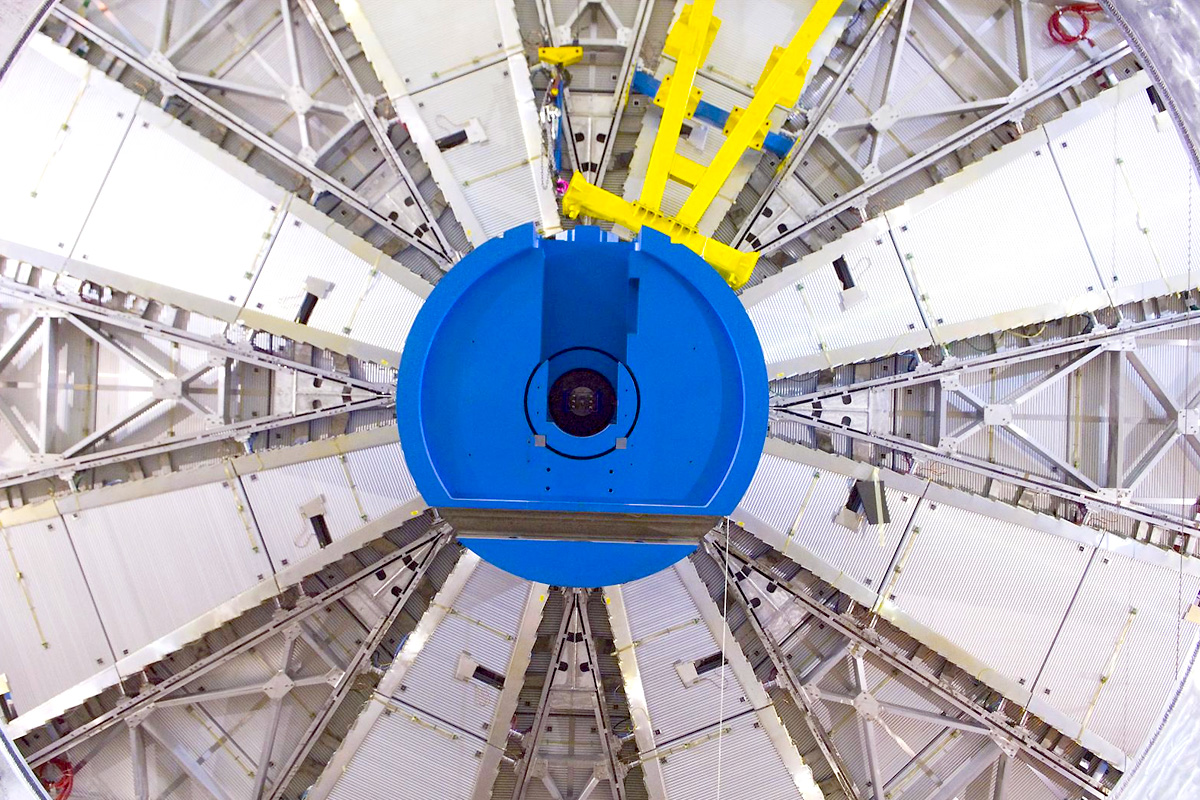

Monitored Drift Tubes
- Measure curves of tracks.
- 1,171 chambers with total 354,240 tubes (3 cm diameter, 0.85-6.5 m long).
- Tube resolution 80 μm
Cathode Strip Chambers
- Measure precision coordinates at ends of detector.
- 70,000 channels
- Resolution 60 μm