Access to Collaboration Site and Physics Results
Magnet System
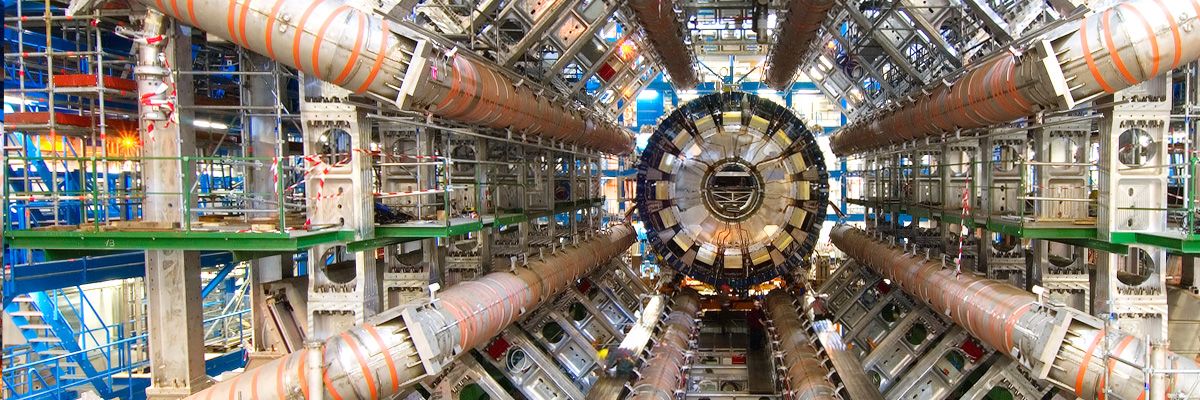
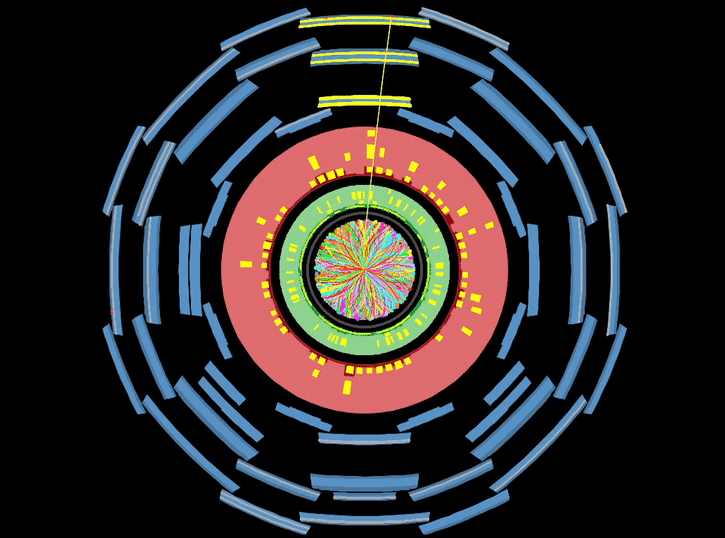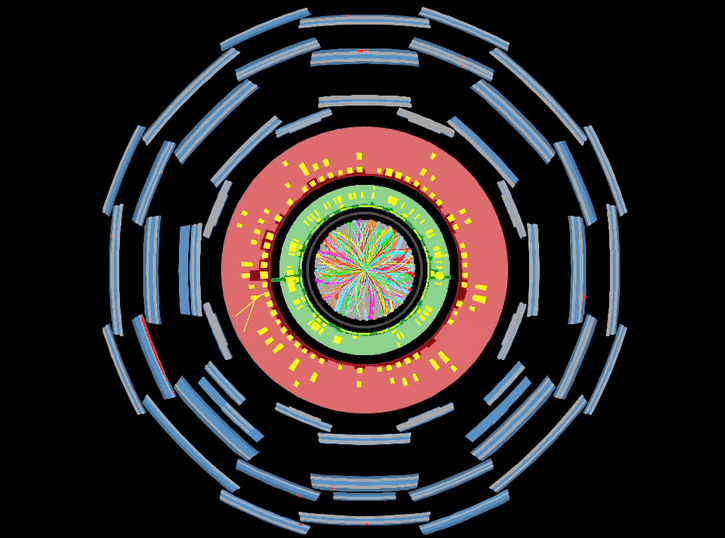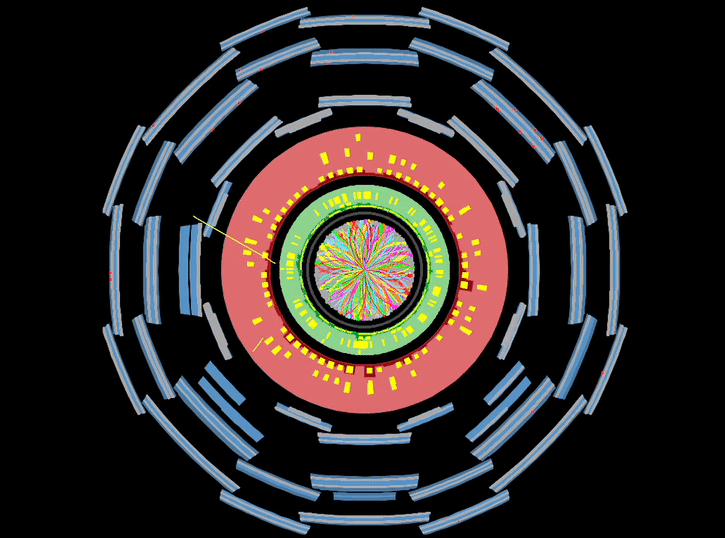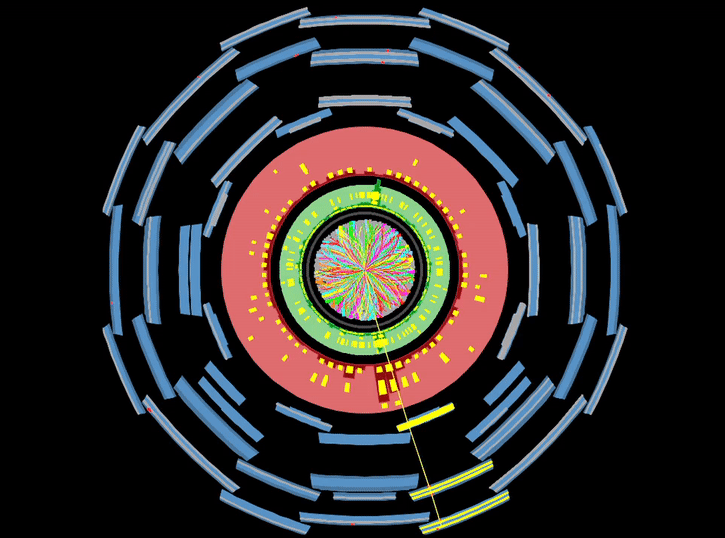
The magnet system of ATLAS bends particles around the various layers of detector systems, making it easier to contain the tracks of particles. The main sections of the magnet system are: Central Solenoid Magnet, Barrel Toroid and End-cap Toroids.

Barrel Toroid
- 25.3 m length
- 20.1 m outer diameter
- 8 separate coils
- 1.08 GJ stored energy
- 370 tonnes cold mass
- 830 tonnes weight
- 4 T magnetic field on superconductor
- 56 km Al/NbTi/Cu conductor
- 20.5 kA nominal current
- 4.7 K working point temperature
- 100 km superconducting wire

End-cap Toroid
- 5.0 m axial length
- 10.7 m outer diameter
- 8 coils in a common cryostat each
- 0.25 GJ stored energy in each
- 160 tonnes cold mass each
- 240 tonnes weight each
- 4 T magnetic field on superconductor
- 13 km Al/NbTi/Cu conductor each
- 20.5 kA nominal current
- 4.7 K working point temperature

Central Solenoid Magnet
- Bends charged particles for momentum measurement
- 5.3 long, 2.4 m diameter, 4.5 cm thick
- 5 tonne weight
- 2 tesla (T) magnetic field with a stored energy of 38 megajoules (MJ)
- 9 km of superconducting wire
- Nominal current: 7.73 kiloampere (kA)
Descent of the eighth and final coil of the ATLAS barrel toroid into the experimental cavern. (August 2005)
After many technical trials and tribulations and an 80-m descent, the vast end-cap of the ATLAS toroid magnet was installed in the experimental cavern.