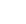Access to Collaboration Site and Physics Results

New ATLAS members, welcome on board
– This summer was rich with events regularly organised by the ATLAS Early Career Scientists Board (ECSB): Induction Day, Career Q&A and the Ice Cream event. The ECSB is a special advisory group dedicated to assisting the ATLAS Collaboration in building an environment where the full scientific potential of young scientists can be realised. It consists of seven early career scientists, representing various career levels, nationalities, genders and home institutions. I have been in the thick of things as a new member of the ECSB and had a lot of new experiences. Each event was full of fantastic people and brought to its participants tonnes of useful information.Read more →

ATLAS Experiment welcomes the public for CERN Open Days
– The ATLAS Experiment will be opening its doors to the world on 14 and 15 September 2019 for the CERN Open Days. This weekend-long event will be an exciting opportunity for members of the public to explore the world’s largest particle-physics laboratory – host to the most powerful particle accelerator ever built, the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) – and take part in over 100 activities around the CERN campus.Read more →
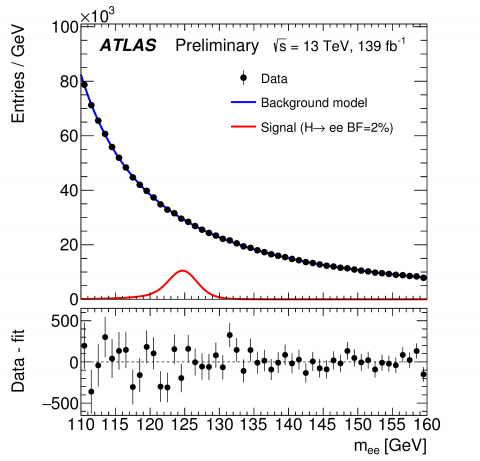
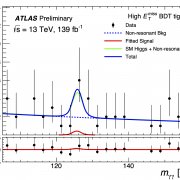
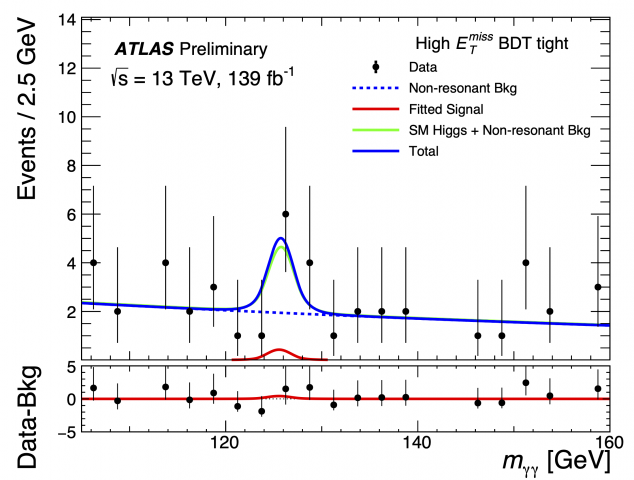
Searching for Higgs boson interactions with the lightest charged lepton
– Does the Higgs boson follow all of the rules set by the Standard Model? Since discovering the particle in 2012, the ATLAS and CMS Collaborations have been hard at work studying the behaviour of the Higgs boson. Any unexpected observations could be a sign of new physics beyond the Standard Model.Read more →
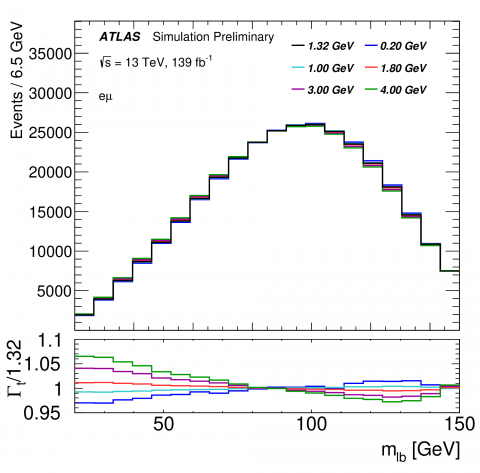
ATLAS delivers new direct measurement of the top-quark decay width with improved precision
– As the heaviest known particle, the top quark plays a key role in studies of fundamental interactions. Due to its short lifetime, the top quark decays before it can turn into a hadron. Thus, its properties are preserved and transferred to its decay products, which can in turn be measured in high-energy physics experiments. Such studies provide an excellent testing ground for the Standard Model and may provide clues for new physics.Read more →
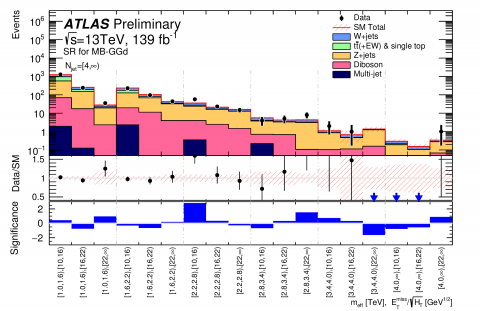
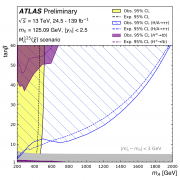
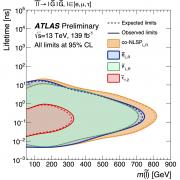
ATLAS releases new search for strong supersymmetry
– New particles sensitive to the strong interaction might be produced in abundance in the proton-proton collisions generated by the LHC – provided that they aren’t too heavy. These particles could be the partners of gluons and quarks predicted by supersymmetry (SUSY), a proposed extension of the Standard Model of particle physics that would expand its predictive power to include much higher energies. In the simplest scenarios, these “gluinos” and “squarks” would be produced in pairs, and decay directly into quarks and a new stable neutral particle (the “neutralino”), which would not interact with the ATLAS detector. The neutralino could be the main constituent of dark matter.Read more →

Zooming in on top-quark production
– As the heaviest known elementary particle, the top quark has a special place in LHC physics. Top quark-antiquark pairs are copiously produced in collisions recorded by the ATLAS detector, providing a rich testing ground for theoretical models of particle collisions at the highest accessible energies. Any deviations between measurements and predictions could point to shortcomings in the theory – or first hints of something completely new.Read more →

A golden era of exploration: ATLAS highlights from EPS-HEP 2019
– Eight years of operation. Over 10,000 trillion high-energy proton collisions. One critical new particle discovery. Countless new insights into our universe. The Large Hadron Collider (LHC) has been breaking records since data-taking began in 2010 – and yet, for ATLAS and its fellow LHC experiments, a golden era of exploration is only just beginning.Read more →
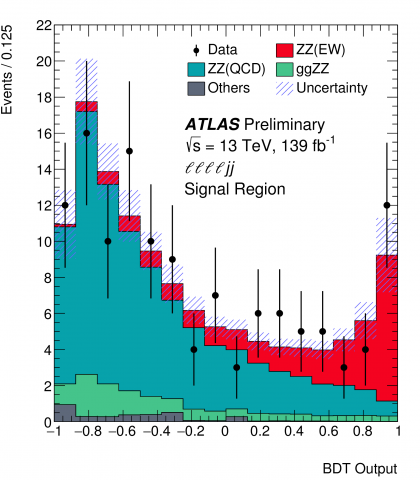
New milestone reached in the study of electroweak symmetry breaking
– In the Standard Model of particle physics, elementary particles acquire their masses by interacting with the Higgs field. This process is governed by a delicate mechanism: electroweak symmetry breaking (EWSB). Although EWSB was first proposed in 1964, it remains among the least understood phenomena of the Standard Model as a large dataset of high-energy particle collisions is required to probe it.Read more →
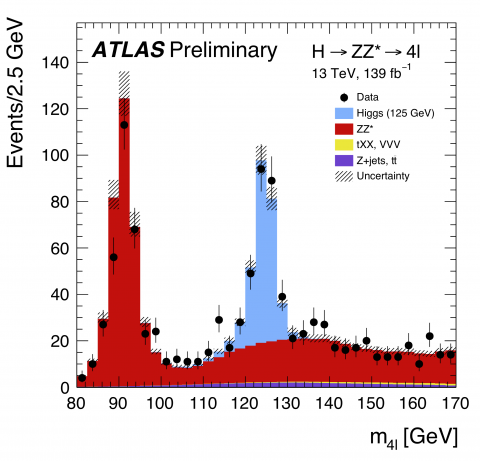
Exploring the Higgs boson “discovery channels"
– This week, at the European Physical Society Conference on High-Energy Physics (EPS-HEP) in Ghent, Belgium, the ATLAS Collaboration at CERN released new measurements of Higgs boson properties using the full LHC Run 2 dataset. Critically, the new results examine two of the Higgs boson decays that led to the particle’s discovery in 2012: H→ZZ*→4ℓ, where the Higgs boson decays into two Z bosons, in turn decaying into four leptons (electrons or muons); and H → γγ, where the Higgs boson decays directly into two photons.Read more →
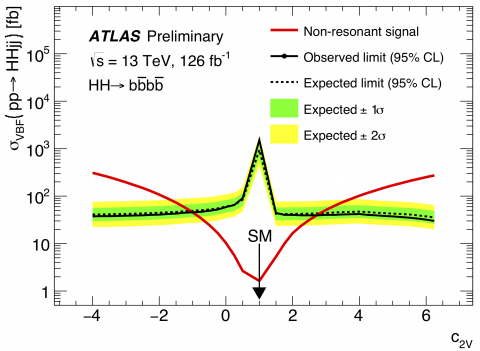
Double the Higgs for double the difficulty
– A key interaction not yet observed by LHC experiments is the production of “double Higgs”. The Standard Model predicts that the Higgs field can interact with itself to create a Higgs boson pair. The rate with which this happens is critical, as it allows physicists to directly probe the potential energy of the Higgs field, which is responsible for mass of particles. Deviations from the expectation would be a strong hint of new physics.Read more →