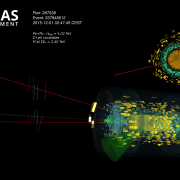
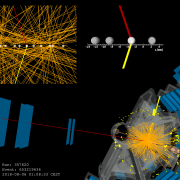
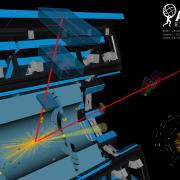
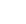Access to Collaboration Site and Physics Results
Updates tagged: “EPS”
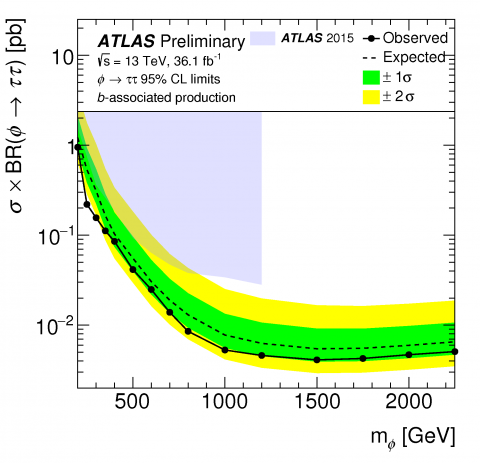
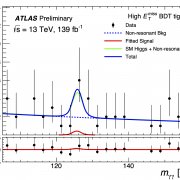
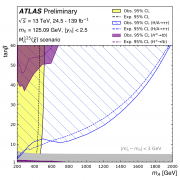
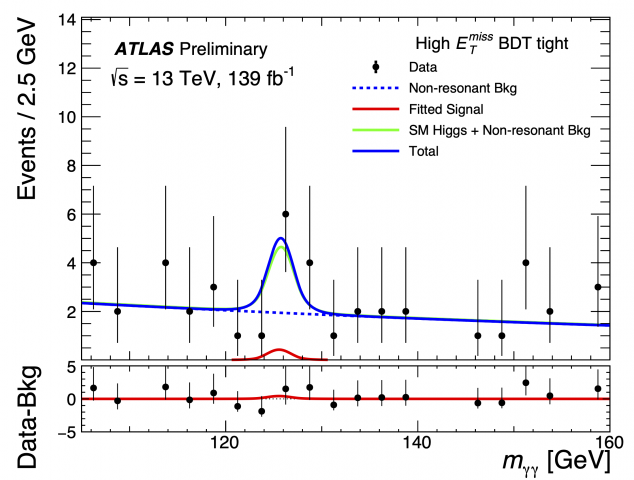
Why should there be only one? Searching for additional Higgs Bosons beyond the Standard Model
Since the discovery of the elusive Higgs boson in 2012, researchers have been looking beyond the Standard Model to answer many outstanding questions. An attractive extension to the Standard Model is Supersymmetry (SUSY), which introduces a plethora of new particles, some of which may be candidates for Dark Matter.
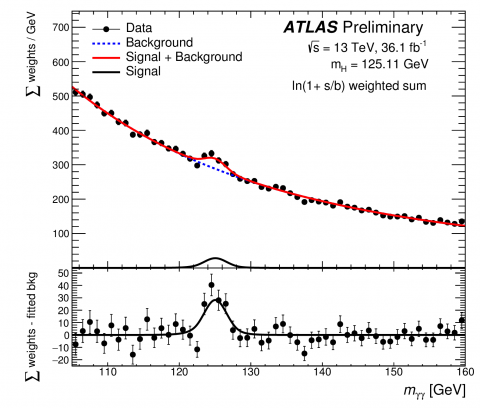
New ATLAS measurement of the Higgs Boson mass
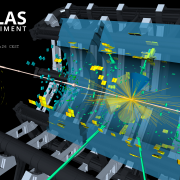
The ATLAS collaboration has released a new preliminary measurement of the Higgs boson mass using 2015 and 2016 LHC data. The number of recorded Higgs boson events has more than tripled since the first measurement of the Higgs boson was released, using 2011/2012 data. An improved precision in the measurement of the Higgs boson mass has been made possible by both the increased collision energy of 13 TeV and improved collision rate.
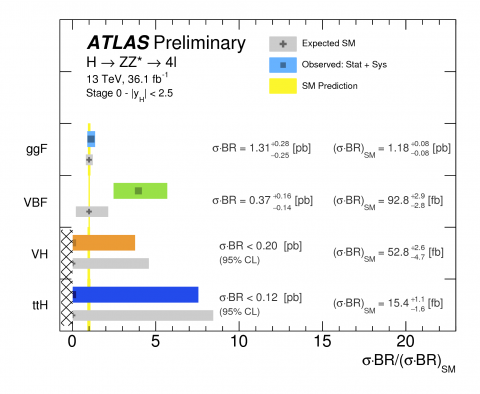
ATLAS takes a closer look at the Higgs boson’s couplings to other bosons
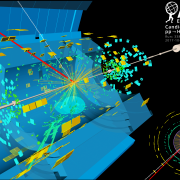
Since resuming operation for Run 2, the LHC has been producing about 20,000 Higgs bosons per day in its 13 TeV proton–proton collisions. At the end of 2015, the data collected by the ATLAS and CMS collaborations were already enough to re-observe the Higgs boson at the new collision energy. Now, having recorded more than 36,000 trillion collisions between 2015 and 2016, ATLAS can perform ever more precise measurements of the properties of the Higgs boson
Chasing the invisible
Cosmological and astrophysical observations based on gravitational interactions indicate that the matter described by the Standard Model of particle physics constitutes only a small fraction of the entire known Universe. These observations infer the existence of Dark Matter, which, if of particle nature, would have to be beyond the Standard Model.
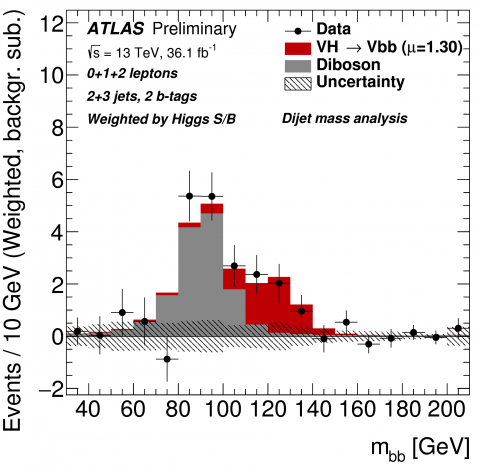
A first LHC sighting of the Higgs boson in its favourite decay
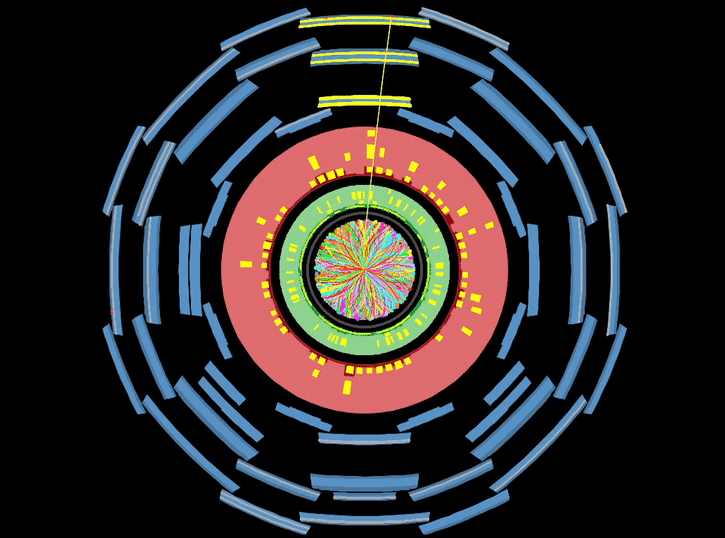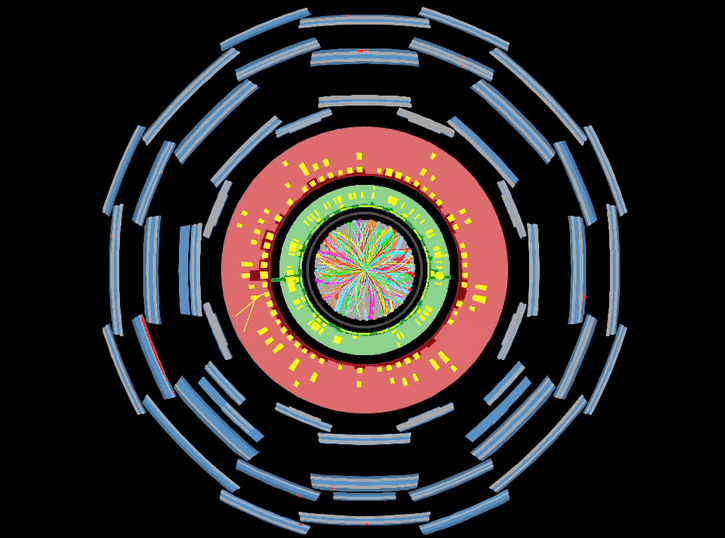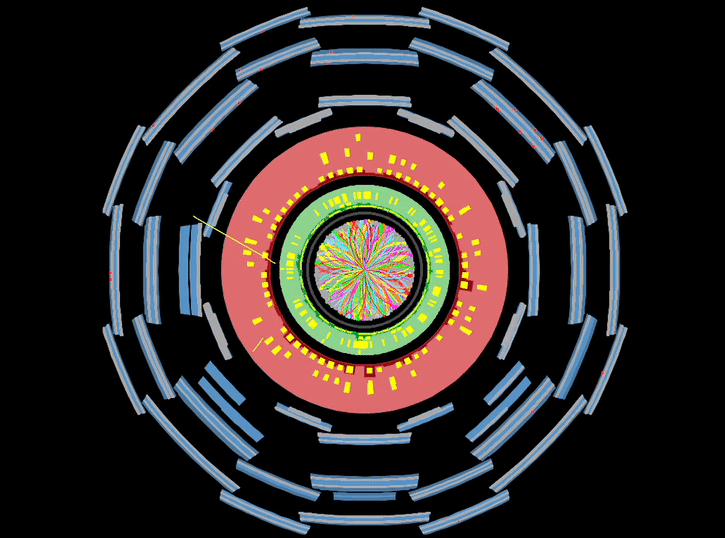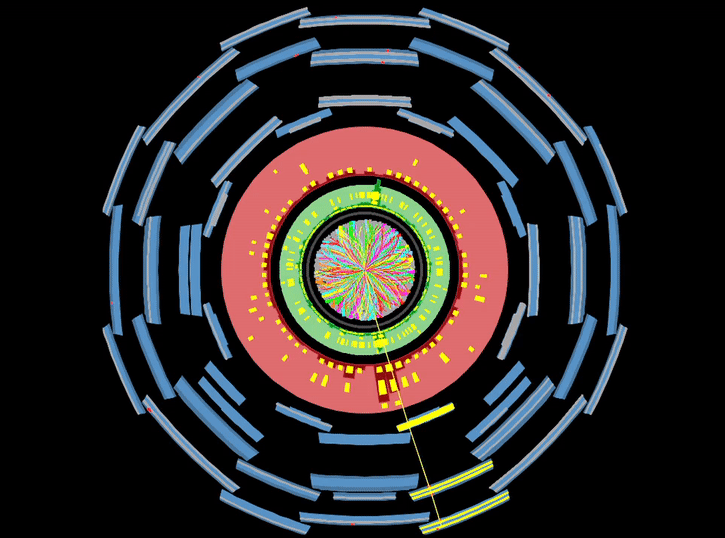
Until now, the Higgs boson had been observed decaying to photons, tau-leptons, and W and Z bosons. However, these impressive achievements represent only 30% of the Higgs boson decays! The Higgs boson’s favoured decay to a pair of b-quarks, which was predicted to happen around 58% of the time and thus drives the short lifetime of the Higgs boson, had so far remained elusive. Observing this decay would fill in one of the big missing pieces of our knowledge of the Higgs sector. It would confirm that the Higgs mechanism is responsible for the masses of quarks and might also provide hints of new physics beyond our current theories. All in all, it is a vital missing piece of the Higgs boson puzzle!

Q&A with EPS Outreach Award-Winner Kate Shaw
ATLAS Outreach Co-coordinator Kate Shaw has been awarded the 2015 European Physical Society (EPS) Outreach prize "for her contributions to the International Masterclasses and for her pioneering role in bringing them to countries with no strong tradition in particle physics".
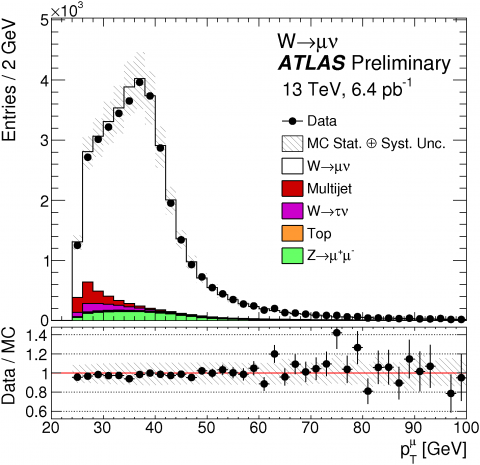
Physics and performance with 13 TeV proton collisions
After a shutdown of more than two years, Run 2 of the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) has restarted with proton–proton collisions at a centre-of-mass energy of 13 TeV. This new phase will allow the LHC experiments to explore nature and probe the physical laws governing it at scales never reached before.
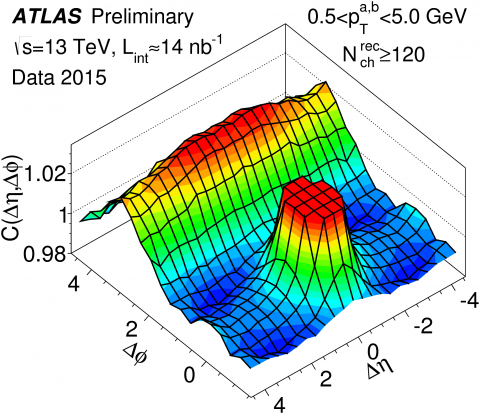
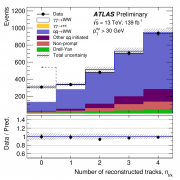
ATLAS measurements of the ridge in proton-proton collisions at 13TeV
Previous studies of two-particle angular correlations in proton-proton, proton-lead, and lead-lead collisions at the LHC have provided important insight on the physics of the particle production process. On 24 July, Atlas presented new preliminary measurements of two-particle correlations...
Of mesons and bosons
ATLAS is ready for detailed physics studies. The experiment used early data collected from the LHC’s Run 2 to calibrate its detectors. Measurements of the production and leptonic decay of certain particle resonances have shown that the detectors and software are working as expected.
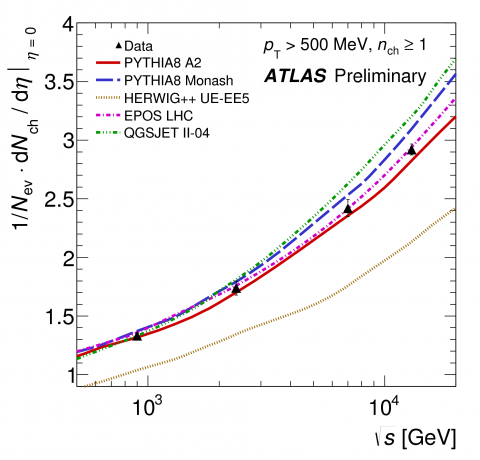
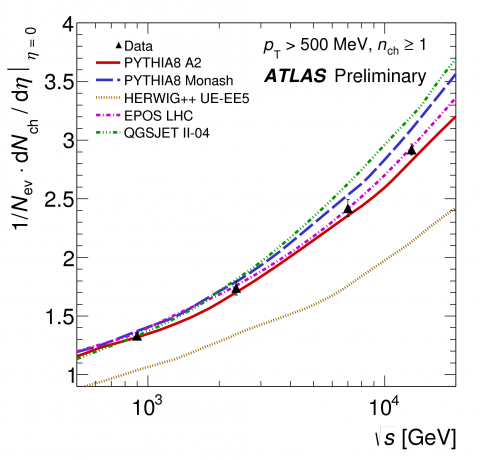
Early Run 2 results test event generator energy extrapolation
On 23 July 2015, ATLAS presented its first measurements of soft strong interaction processes using charged particles produced in proton–proton collisions at 13 TeV centre-of-mass energy delivered by the Large Hadron Collider at CERN. These measurements were performed with a dataset collected beginning of June under special low-luminosity conditions.