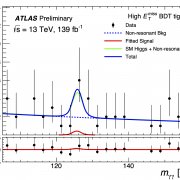
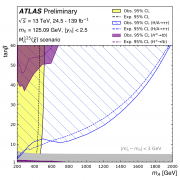
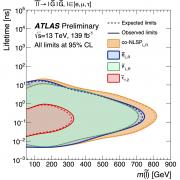
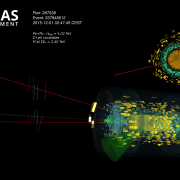
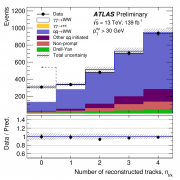
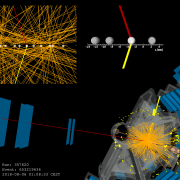
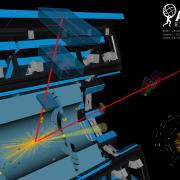
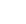Access to Collaboration Site and Physics Results
Updates tagged: “Combined Performance”
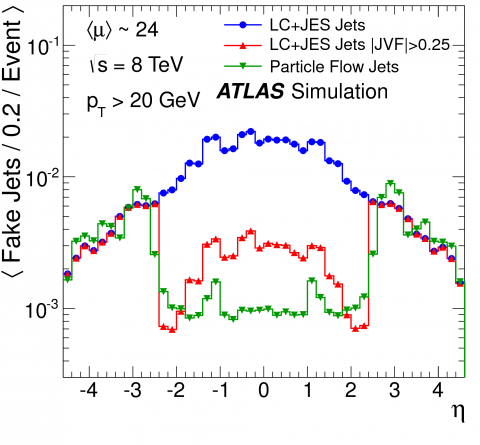
Making the most of the ATLAS detector
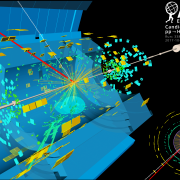
Up to now, ATLAS has measured the energies and positions of jets using the finely segmented calorimeter system, in which both electrically charged and neutral particles interact. However, the inner detector tracking system provides more precise measurements of charged particle energies and positions. A recent ATLAS paper describes a particle flow algorithm that extrapolates the charged tracks seen by the inner detector to the calorimeter regions.
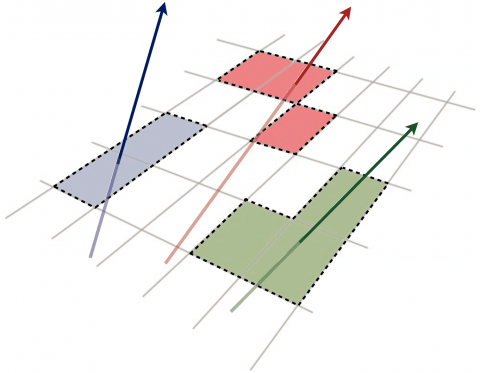
Charged-particle reconstruction at the energy frontier
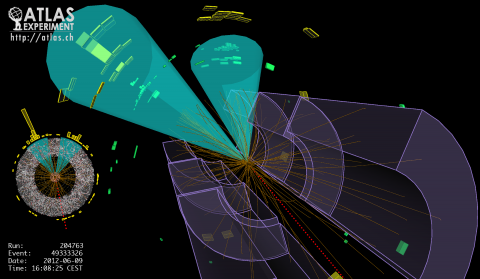
A new age of exploration dawned at the start of Run 2 of the Large Hadron Collider, as protons began colliding at the unprecedented centre-of-mass energy of 13 TeV. The ATLAS experiment now frequently observes highly collimated bundles of particles (known as jets) with energies of up to multiple TeV, as well as tau-leptons and b-hadrons that pass through the innermost detector layers before decaying. These energetic collisions are prime hunting grounds for signs of new physics, including massive, hypothetical new particles that would decay to much lighter – and therefore highly boosted – bosons.
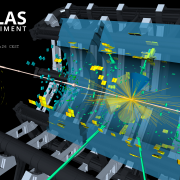
What happens when energy goes missing?
Here at ATLAS, we like to consider ourselves pretty decent at tracking down particles. In fact, we do it every day. Just because a proton-proton collision doesn’t produce the next Nobel Prize winning particle doesn’t mean we can ignore it. Teams of physicists are still combing through every single event, rebuilding known particles out of the signals they leave us
Stacking the building blocks of the 2016 ATLAS physics programme
2016 is set to be an outstanding year for the ATLAS experiment and the Large Hadron Collider. We’re expecting up to 10 times more data compared to 2015, which will allow us to make precise measurements of many known physics processes and to search for new physics.

A boost for the next discovery
I arrived in Chicago for my first conference after the first long LHC shutdown, where new results from the two big experiments ATLAS and CMS were to be shown. Before the beginning of the conference on Monday, I had one day to fight against jetlag and see the city – certainly not enough time to see everything!

Boost and never look back
When I arrived in Chicago this last Sunday for the BOOST conference I had a pretty good idea what new results we were going to show from ATLAS. I also had some rough ideas of what our friends from the other experiments and theory groups would be up to. What I didn’t expect was to see an ad that would fit the conference so nicely!

ATLAS awards Long Shutdown 1 achievements
The ATLAS Outstanding Achievement Awards 2015 were presented on 18 June to 26 physicists and engineers, in 11 groups, for their excellent work carried out during Long Shutdown 1 (LS1).
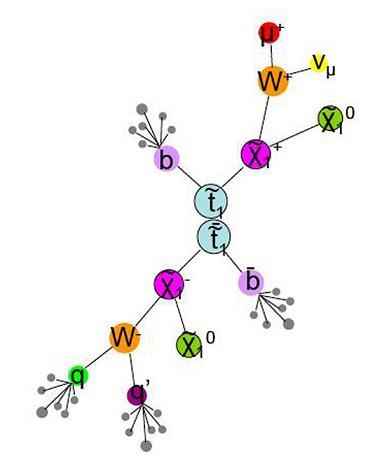
From 0-60 in 10 million seconds! – Part 2
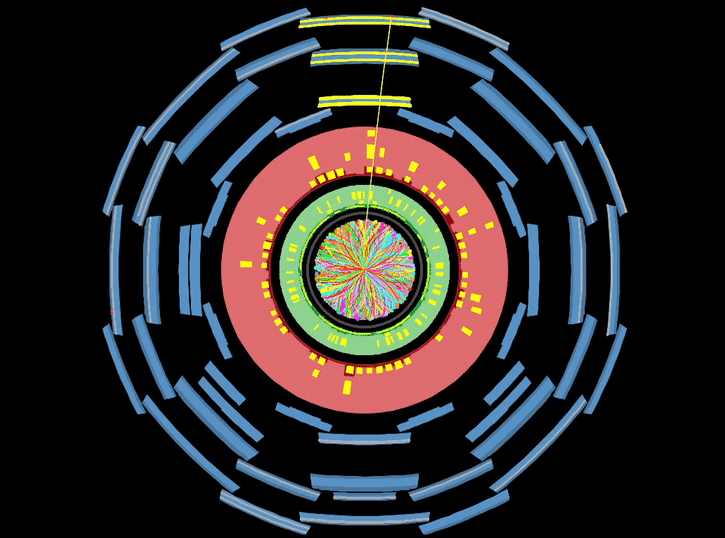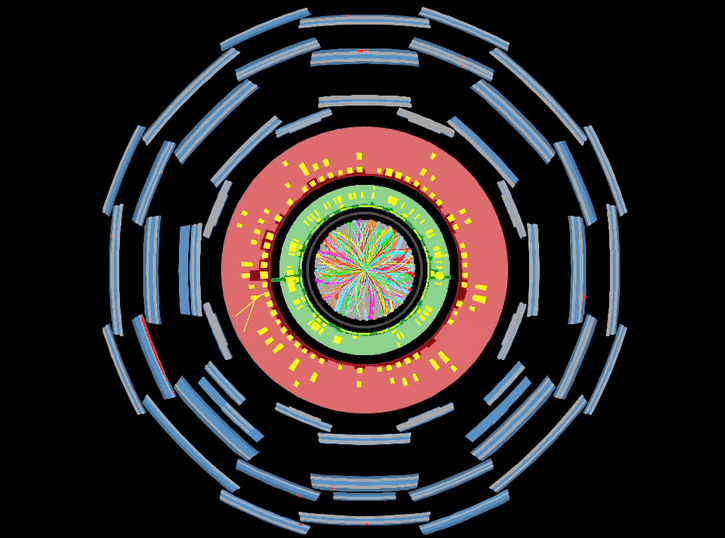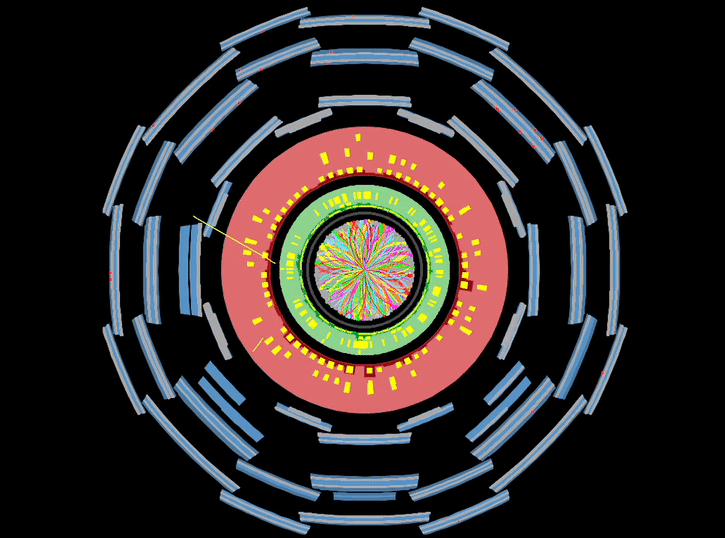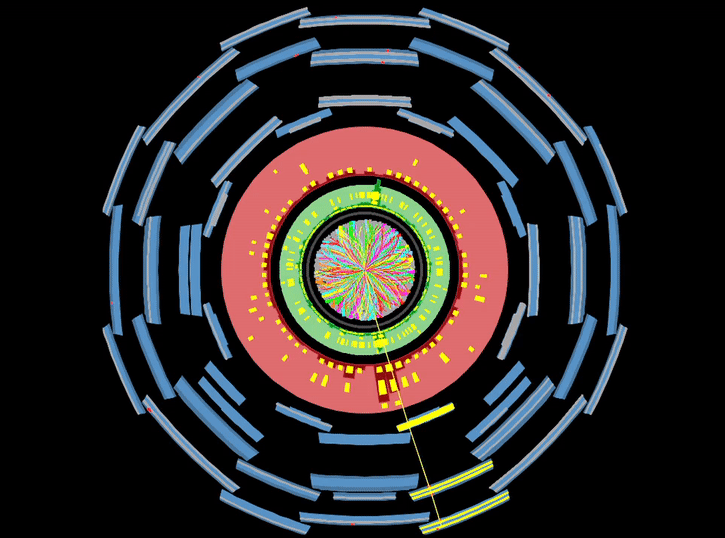
This is continuing from the previous post, where I discussed how we convert data collected by ATLAS into usable objects. Here I explain the steps to get a Physics result. I can now use our data sample to prove/disprove the predictions of Supersymmetry (SUSY), string theory or what have you. What steps do I follow?
From 0-60 in 10 million seconds! – Part 1
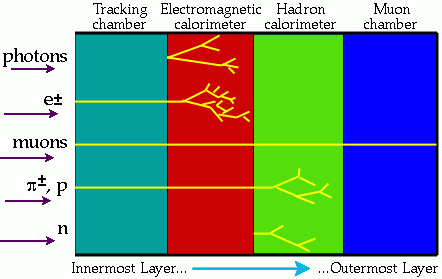
OK, so I’ll try to give a flavour of how the data that we collect gets turned into a published result. As the title indicates, it takes a while! The post got very long, so I have split it in two parts. The first will talk about reconstructing data, and the second will explain the analysis stage.