Access to Collaboration Site and Physics Results
ATLAS Briefings
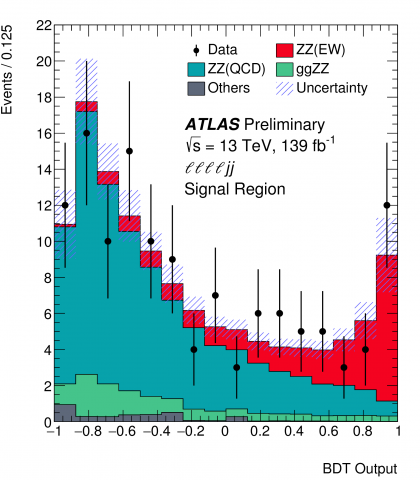
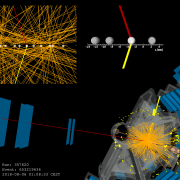
New milestone reached in the study of electroweak symmetry breaking
– In the Standard Model of particle physics, elementary particles acquire their masses by interacting with the Higgs field. This process is governed by a delicate mechanism: electroweak symmetry breaking (EWSB). Although EWSB was first proposed in 1964, it remains among the least understood phenomena of the Standard Model as a large dataset of high-energy particle collisions is required to probe it.Read more →
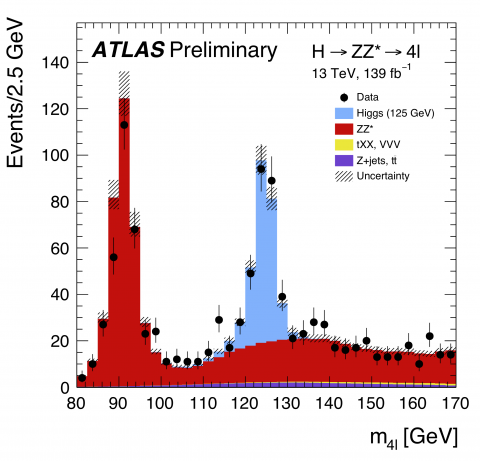
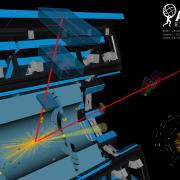
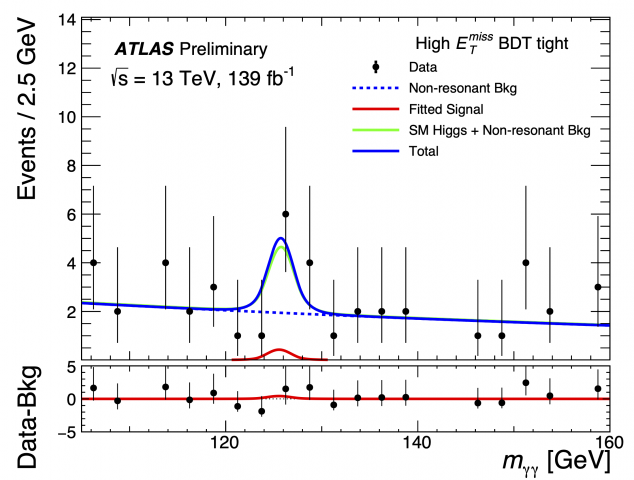
Exploring the Higgs boson “discovery channels"
– This week, at the European Physical Society Conference on High-Energy Physics (EPS-HEP) in Ghent, Belgium, the ATLAS Collaboration at CERN released new measurements of Higgs boson properties using the full LHC Run 2 dataset. Critically, the new results examine two of the Higgs boson decays that led to the particle’s discovery in 2012: H→ZZ*→4ℓ, where the Higgs boson decays into two Z bosons, in turn decaying into four leptons (electrons or muons); and H → γγ, where the Higgs boson decays directly into two photons.Read more →
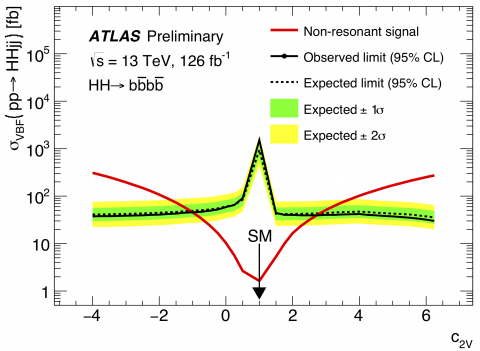
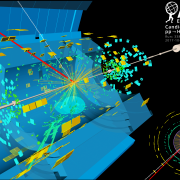
Double the Higgs for double the difficulty
– A key interaction not yet observed by LHC experiments is the production of “double Higgs”. The Standard Model predicts that the Higgs field can interact with itself to create a Higgs boson pair. The rate with which this happens is critical, as it allows physicists to directly probe the potential energy of the Higgs field, which is responsible for mass of particles. Deviations from the expectation would be a strong hint of new physics.Read more →
ATLAS searches for rare Higgs boson decays into muon pairs
– Today, at the European Physical Society Conference on High-Energy Physics (EPS-HEP) in Ghent, Belgium, the ATLAS Collaboration released a new preliminary result searching for Higgs boson decays to a muon and antimuon pair (H → μμ). The new, more sensitive result uses the full Run 2 dataset, analysing almost twice as many Higgs boson events as the previous ATLAS result.Read more →

ATLAS finds evidence of charge asymmetry in top-quark pairs
– Among the most intriguing particles studied by the ATLAS collaboration is the top quark. As the heaviest known fundamental particle, it plays a unique role in the Standard Model of particle physics and – perhaps – in yet unseen physics beyond the Standard Model. A new ATLAS result, presented today at the European Physical Society Conference on High-Energy Physics (EPS-HEP) in Ghent, Belgium, examines the full Run 2 dataset to find evidence of charge asymmetry in top-quark pair events, with a significance of four standard deviations.Read more →

ATLAS delivers its most precise luminosity measurement yet
– The large amount of data delivered by the LHC in Run 2 (2015-2018) has not only allowed the ATLAS Experiment to probe previously unexplored territory for rare Standard Model processes and new physics, but also to measure already known processes to better precision. In both cases, but particularly the latter, a precise measurement of the integrated luminosity of the dataset is essential. In other words, how many proton collisions actually occurred in ATLAS during Run 2.Read more →
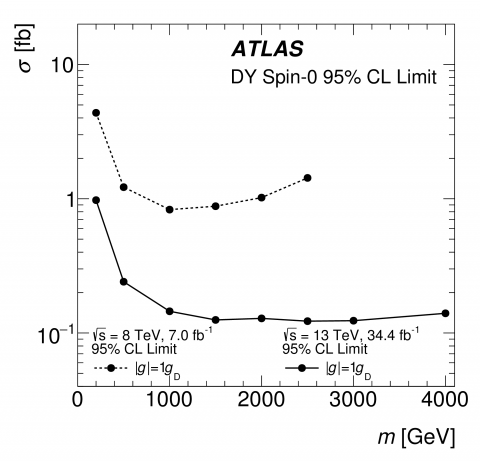
ATLAS releases new result in hunt for mysterious magnetic monopoles
– Dipole magnets are probably the best-known source of magnetic fields. They consist of a north and south pole; while one end magnetically attracts, the opposite repels. If you cut a magnet in half, you are left with two magnets, each with its own north and south pole. This apparent absence of an isolated magnetic pole - or “magnetic monopole” - has puzzled physicists for more than a century. It would seem perfectly natural for this particle to be present in our universe; Maxwell’s equations would reflect complete symmetry between electricity and magnetism if particles with magnetic charge were observed. So far the mystery remains: while every known particle in our universe is either electrically charged or neutral, none have been found to be magnetically charged.Read more →
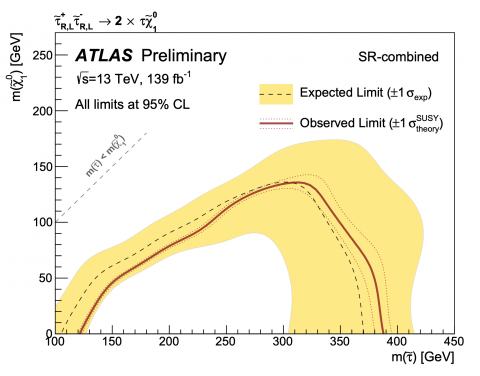
Searching for Electroweak SUSY: not because it is easy, but because it is hard
– Today, at the Large Hadron Collider Physics (LHCP) conference in Puebla, Mexico, and at the SUSY2019 conference in Corpus Christi, USA, the ATLAS Collaboration presented numerous new searches for SUSY based on the full Run-2 dataset (taken between 2015 and 2018), including two particularly challenging searches for electroweak SUSY. Both target particles that are produced at extremely low rates at the LHC, and decay into Standard Model particles that are themselves difficult to reconstruct. The large amount of data successfully collected by ATLAS in Run 2 provides a unique opportunity to explore these scenarios with new analysis techniques.Read more →
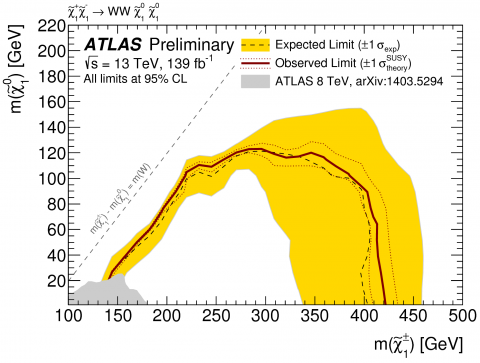
ATLAS sets strong constraints on supersymmetric dark matter
– One of the most complete theoretical frameworks that includes a dark matter candidate is supersymmetry. Dark matter is an unknown type of matter present in the universe, which could be of particle origin. Many supersymmetric models predict the existence of a new stable, invisible particle - the lightest supersymmetric particle (LSP) – which has the right properties to be a dark matter particle. The ATLAS Collaboration has recently reported two new results on searches for an LSP where it exploited the experiment’s full “Run 2” data sample taken at 13 TeV proton-proton collision energy. The analyses looked for the pair production of two heavy supersymmetric particles, each of which decays to observable Standard Model particles and an LSP in the detector.Read more →
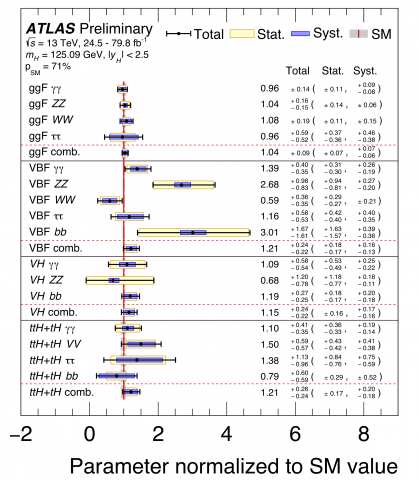
All together now: adding more pieces to the Higgs boson puzzle
– The Higgs boson was discovered in 2012 by the ATLAS and CMS experiments, but its rich interaction properties (its coupling to other particles) have remained a puzzle. Thanks to an unprecedented amount of Higgs bosons produced at the LHC, all of the main Higgs boson production and decay modes have now been observed.Read more →