Access to Collaboration Site and Physics Results
ATLAS Collaboration
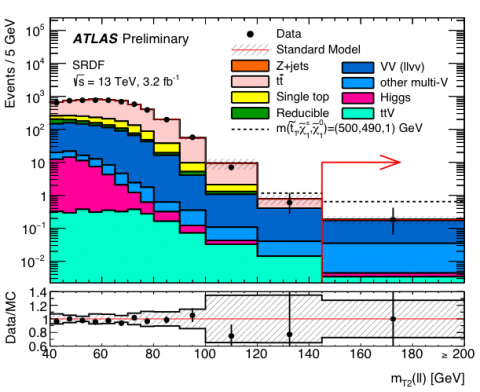
Wanted: SUSY particle still at large
According to classical electrodynamics, the electromagnetic energy (and mass) of a point-like electron should be infinite. This is of course not the case! The solution of the riddle is antimatter - the ‘vacuum’ around every electron is filled with a cloud of electrons and anti-electrons and the combined energy turns out to be finite.
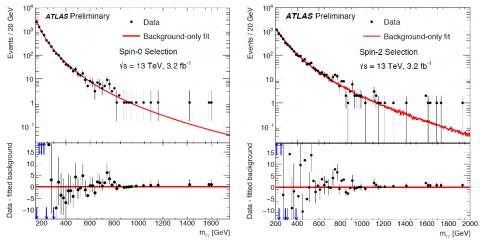
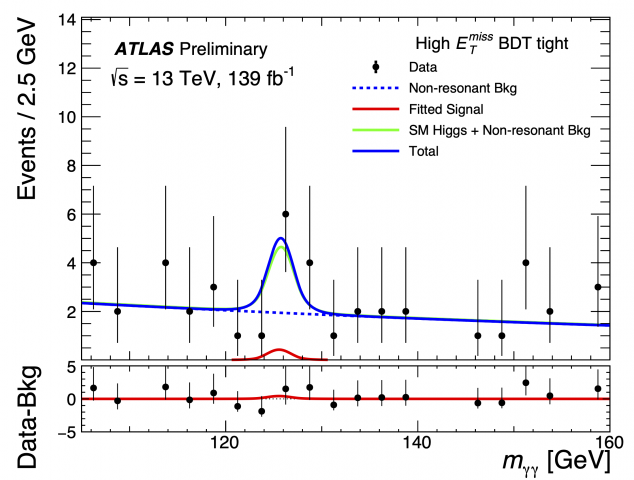
Searching beyond the Standard Model with photon pairs
The ATLAS Collaboration uses two selections in this search, one optimised for Higgs-like particles that are expected to have a strong signal compared to background with both photons in the central region of the detector (the “spin-0” selection) and a second optimised for graviton-like particles (the “spin-2” selection) which often have at least one photon close to the LHC proton beam axis.
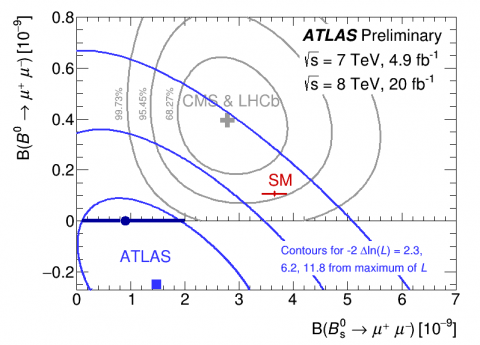
Chasing after elusive B meson decays into muons
Almost four years following the discovery of the Higgs boson, LHC experiments are now more than ever exploring the possibility of new particles and new effects beyond the Standard Model.
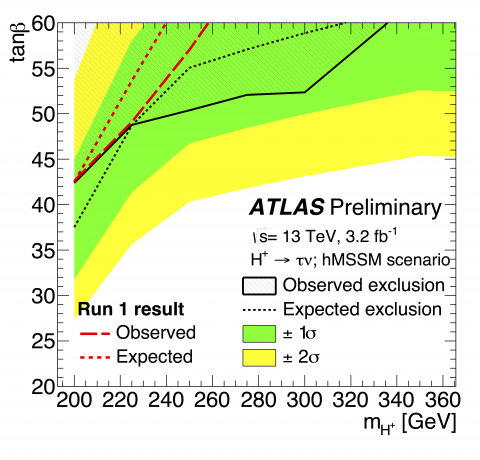
Are there more Higgs bosons?
The results presented by the ATLAS collaboration during the Moriond Electroweak 2016 conference set new limits on a potential extended Higgs sector.

ATLAS announces Thesis Award winners
On 25 February 2016 in CERN's Main Auditorium, the ATLAS collaboration announced the winners of the 2015 ATLAS Thesis Awards: Javier Montejo Berlingen, Ruth Pöttgen, Nils Ruthmann, and Steven Schramm. The winners were selected by the ATLAS Thesis Awards Committee for their outstanding contributions to the collaboration in the context of a PhD thesis. A total of 33 nominations were received, all of a very high standard and encompassing major achievements in all areas of ATLAS results and activities.
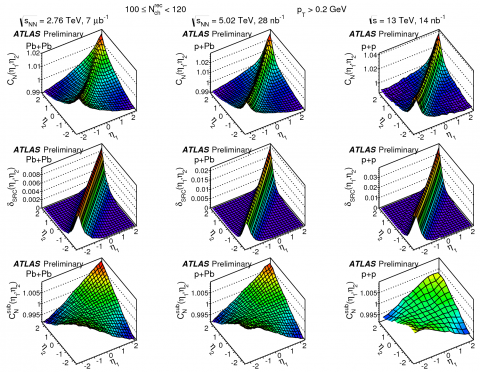
New ATLAS results presented at Quark Matter 2015
Heavy-ion physics is the study of the hot dense medium created shortly after the Big Bang. Physicists examine this medium in three collision systems: lead-lead, proton-lead and proton-proton collisions.
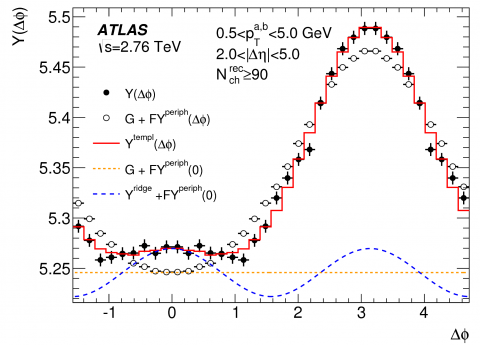
New insight into the proton-proton ridge
The new results confirm that the ridges in proton-proton, proton-nucleus, and nucleus-nucleus collisions have a similar origin. The results also show that the observed weak dependence on the numbers of charged particles and the centre-of-mass energy should provide strong constraints on the mechanism responsible for producing the ridge in proton-proton, and, maybe, proton-nucleus collisions.

ATLAS presents new top physics results
This week, physicists from around the world are gathering at the Top 2015 workshop in Ischia, Italy to discuss the latest measurements of the top quark. As the heaviest known fundamental particle, the top quark plays a special role in the search for "new physics".
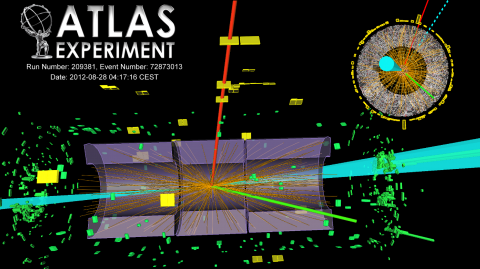
Shedding new light on the Higgs
Today, at the Large Hadron Collider Physics conference (LHCP2015), the ATLAS and CMS collaborations presented the most precise measurements yet of Higgs boson properties. By combining Run 1 data from both experiments, the new measurements paint a clear picture of how the Higgs boson is produced, decays, and interacts with other particles.

Devouring dark matter theories
Most of the matter in the universe is made not of stuff we understand, but of invisible “dark matter” particles. We have yet to observe these mysterious particles on Earth, presumably because they interact so weakly with normal matter. The high energy collisions in the Large Hadron Collider provide our best current hope of making dark matter particles, and thus giving us a better understanding what most of the universe is made of.